Routes of Administration :
The route of administration is determined by properties of the drug (like Water/Lipid soluble , Ionization) and by therapeutic objectives (like need of rapid onset , need of long term onset or restriction of delivery to local site).
=> Major route for drug administration are Enteral, Parental, and topical.
1) Enteral :
Enteral administration (adminstering a drug by mouth) is the most common, convenient, and economical method of drug administration.
=> The drug may be swallowed, allowing oral delivery, or it may be placed under tongue (sublingual) or between the gums and cheek(buccal), facilitating the direct absorption in to blood stream.
(1) ORAL :
• Oral administration provide many advantages like:
(i) Most convenient method for patient.
(ii) these drugs are self administered.
(iii) Toxicities or over dose of oral drug may be overcome with antidotes, such as activated charchol.
(iv) Delivery in circulation is very fast thatswhy rapid and high concentration is avoided which cause less adverse effect.
• There are also some disadvantages for oral route like:
(i) oral drug absorption is very complicated. Bacause of low gastric pH which cause inactivation of drugs.
(ii) GI irritation is common.
(iii) First pass effect decrease the concentration of drug before it reaches the site of action.
=> A wide range of oral preparations is available including enteric coated and extended release preparation.
(a) Enteric coating : it is a chemical envelope that protect the drug from stomach acid.
• It is used for certain drugs which are acid labile (Eg: Omeperazole) and for the drugs which are stomach irritating (like : Aspirin).
(b) extended release preparation : these drugs have special type of coating or ingredients that control drug, thereby allowing for slower absorption and prolonged duration of action.
(2) SUBLINGUAL / BUCCAL :
• Sublingual route involves the placement of drug under the tongue. And Buccal route involves placement of drug between cheek and gum.
=> Both sublingual and buccal route of absorption have many advantages like :
(i) Ease of administration
(ii) Rapid absorption (can be used in emergencies)
(iii) can be terminated by spitting out the drug
(iv) bypass the harsh gastronintestinal environment
(v) avoid the first pass effect
=>There are also some disadvantages of this route like:
(i) Repeated adminstration damage oral mucosa
(ii) Irritation of oral mucosa amd excessive salivtion
(iii) Large doses can not be administered.
(3) RECTAL :
• This route of adminstration is effective in patient with vomiting.
• Drug irritant to stomach can be given by this route.
• Uncooperative and unconscious patient may require administration by this route.
• In this absorption is imperfect.
• rectal inflammation may occurs with repaeated adminstration.
(2) PARENTAL :
• The parental route introduce drugs directly into systemic circulation. This is used for the drugs that are poorly absorbed from the GI tract. (Eg : Heparin) or unstable in the GI tract (Eg : insulin).
=> parental administration provide the most control over the dose of drug delivered to the body.
=> This route of administration is irreversible and may cause pain, fear, local tissue damage amd infections.
=> The bioavailability os parental route is 100%.
=> First pass effect is avoided.
=> There are four major routes of parental administration are:
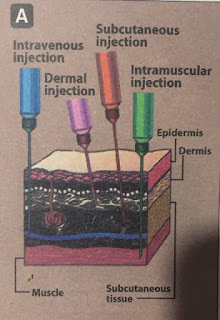
(i) Intravenous
: IV injection is the most common parental route and useful for the drigs which are not absorbed orally.
• IV delivery permits a rapid effect and a maximum degree if control over amount of drug delivered.
•When it is injected as bolus , the full amount is delivered to systemic circulation almost immediately.
(ii) Intramuscular
: Drugs administered IM can be in aqueous solutions, which are absorbed rapidly. or in specialized depot preparations, which are absorbed slowly.
(iii) Subcutaneous
: SC i jection provides absorption via simple diffusion and is slower than IV route.
• This route minimize the risk of thrombosis and hemolysis associated with IV injection and may provide slow and sustained effects.
• This route should not be used with drugs that cause tissue irritation, b/c severe pain and necrosis may occur.
(iv) Intradermal
: It involves injection into dermis, the more vascular layer of skin under epidermis.
• Agents for diagnostic determination and desensitization are usually administered by this route.
(3) Others :
(i) Oral inhalation and nasal preparations :
• Both of these provide rapid absorption of drug across large surface area of mucous membranes of respiratory tract and pulmonery epithelium.
• drugs effects are almost as rapid as IV bolus.
• this route is effective for patients with respiratory disorders such as asthma or COPD b/c drug is delivered directly to the site of action.
(ii) Intrathecal / intraventricular :
• Due to blood brain barrier , drugs are not directly goes to CSF , so this method is used b/c it introduce drug directly in to CSF when rapid effects are needed.
(iii) Transdermal :
• This route achieves systemic effects by application of drugs to the skin, usually via transdermal patch.
• the absorption depends upon:
- physical characterestics of skin at the site of application.
- lipid solubility of drug.







Comments